| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
Tags
- 프로그래머스
- ChatGPT
- 백준
- c++
- 부주상골증후군
- 독일어독학
- 카카오코테
- 롯데정보통신
- DFS
- 독일어
- SWIFT
- sql
- 부주상골수술
- 분할정복
- 리눅스
- SQLD
- istringstream
- dp
- 코딩테스트
- 카카오인턴십
- 코테
- 독학
- 세브란스
- 부주상골수술후기
- 카카오인턴
- 스택
- BFS
- IOS
- 구현
- 부주상골
Archives
- Today
- Total
슈뢰딩거의 고등어
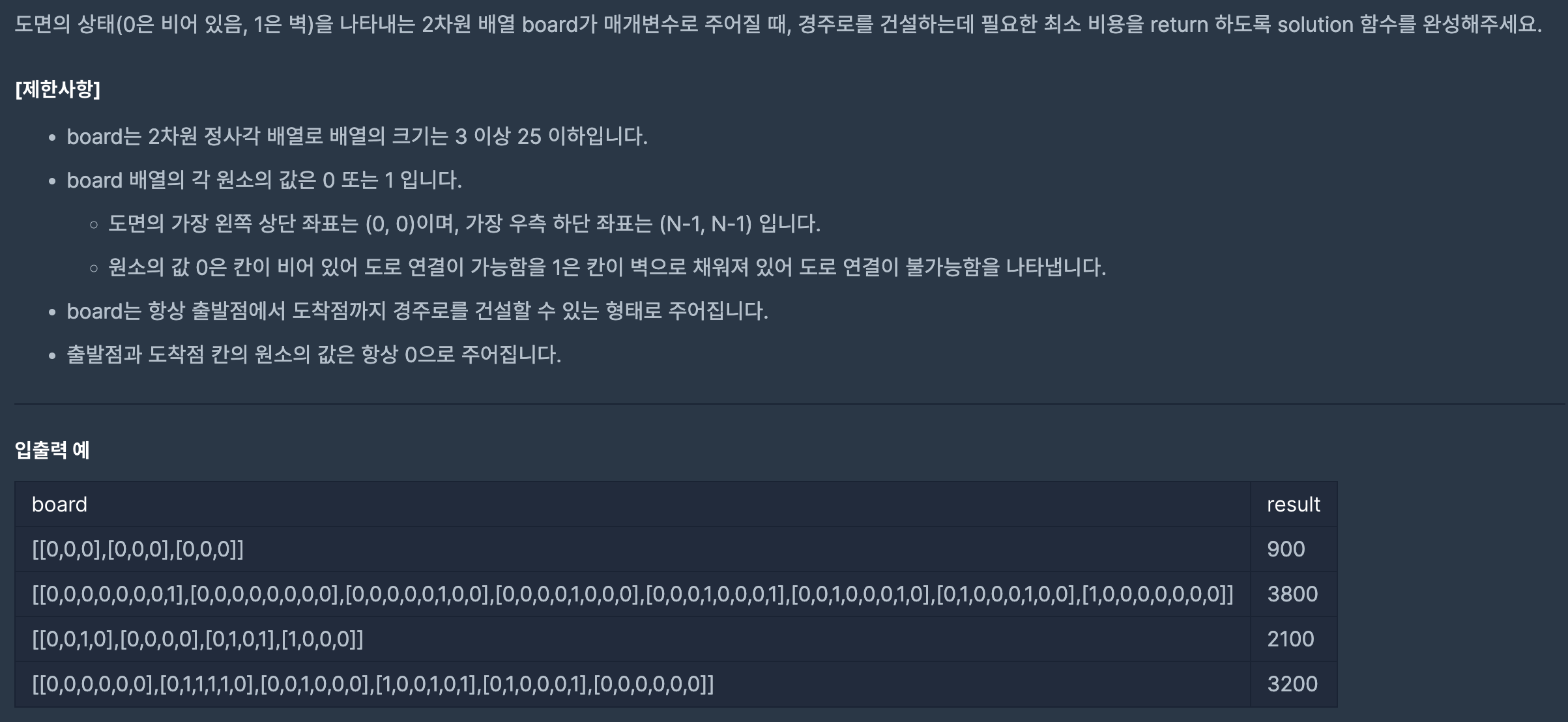
[2020 카카오 인턴십] 경주로 건설 본문
https://programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/67259
코딩테스트 연습 - 경주로 건설
[[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,1,0,0,0,1],[0,0,1,0,0,0,1,0],[0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0],[1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]] 3800 [[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,1],[1,0,0,0]] 2100 [[0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,1,1,1,0],[0,0,1,0,0,0],[1,0,0,1,0,1],[
programmers.co.kr

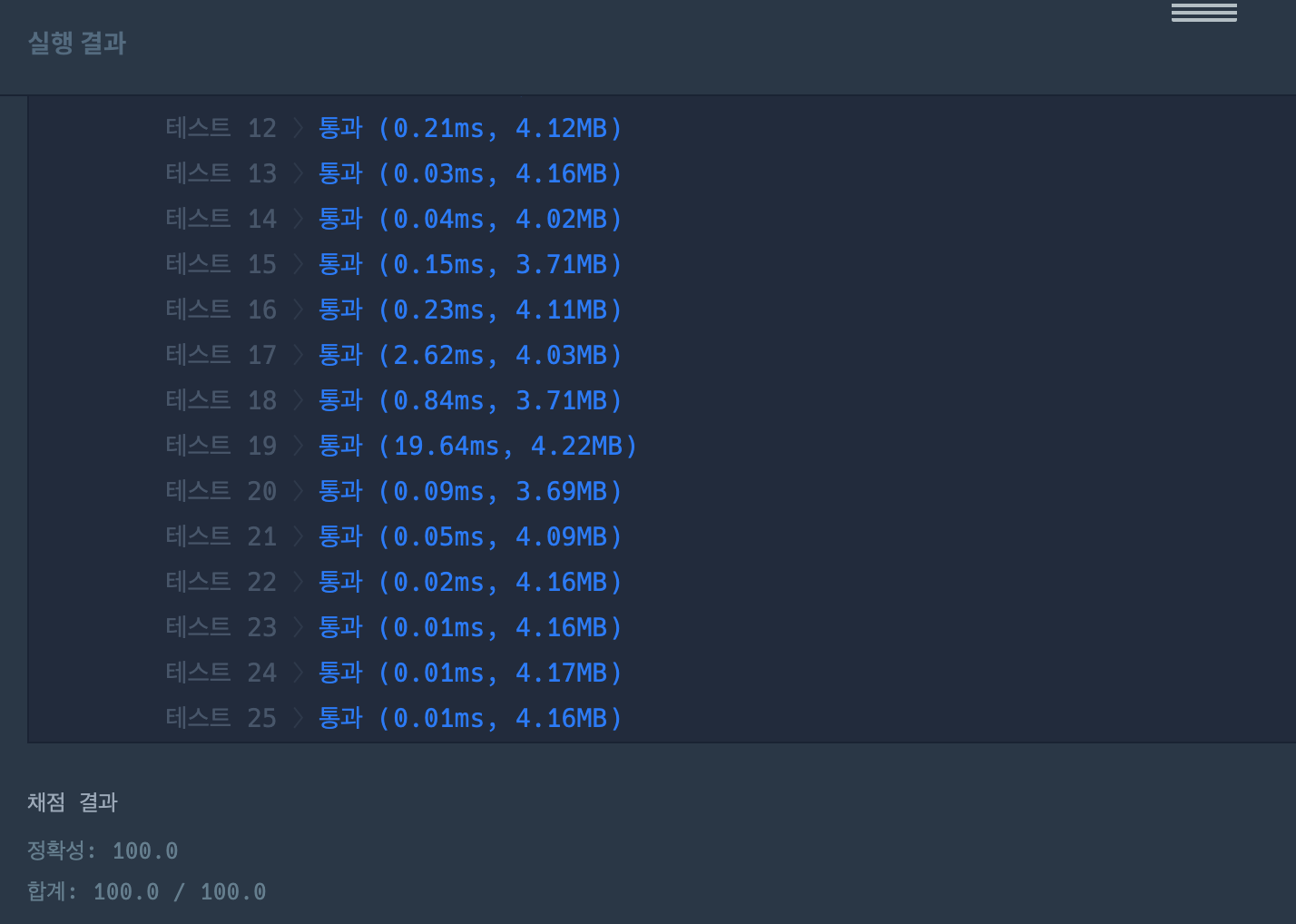
단순히, bfs 로 풀었더니 25번 테스트 케이스가 안맞음
더보기
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct POS {
int y, x, dir, cost;
};
const int dy[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
const int dx[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int solution(vector<vector<int>> board) {
int N = board.size();
int answer = 987654321;
queue <POS> q;
POS start;
start.y = 0; start.x = 0; start.dir = 0; start.cost = 0;
q.push(start);
board[0][0] = 1;
while(!q.empty()) {
POS cur = q.front(); q.pop();
if(cur.y == N-1 && cur.x == N-1) {
answer = min(answer, cur.cost);
}
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int ny = cur.y + dy[i];
int nx = cur.x + dx[i];
if(ny <0 || nx < 0 || ny >= N || nx >= N || board[ny][nx] == 1)
continue;
int ncost = 0;
if(cur.cost != 0 && cur.dir != i) {
ncost = cur.cost + 600;
}
else {
ncost = cur.cost + 100;
}
if(board[ny][nx] == 0 || board[ny][nx] >= ncost) {
POS next;
next.y = ny; next.x = nx; next.dir = i; next.cost = ncost;
q.push(next);
board[ny][nx] = ncost;
}
}
}
return answer;
}결국 다른사람의 풀이를 참고해서 수정 후 통과
실패의 원인은
방향이 cost 에 영향을 주므로, 단순히 그 당시의 최소 비용을 저장하는 것이 아닌 방향정보를 포함해서 맵에 저장할 필요가 있다.
그래서 cost를 방향 정보와 함께 저장하도록 MAP[4][N][N] 를 정의하여 사용한다.
조금 더 효율성을 높이고 싶다면 priority queue 를 사용해서 풀면 최소 cost가 위로 자동으로 정렬이 되기때문에 최초에 N-1, N-1 에 도달한 cost 만 리턴하고 bfs를 종료하는 방식도 있다.
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
struct POS {
int y, x, dir, cost;
};
const int dy[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
const int dx[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int MAP[4][26][26];
int solution(vector<vector<int>> board) {
int N = board.size();
int answer = 987654321;
queue <POS> q;
POS start;
start.y = 0; start.x = 0; start.dir = 1; start.cost = 0;
q.push(start);
start.dir = 3;
q.push(start);
for(int d=0; d<4; d++) {
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
for(int j=0; j<N; j++)
MAP[d][i][j] = 987654321;
}
MAP[1][0][0] = 0;
MAP[3][0][0] = 0;
while(!q.empty()) {
POS cur = q.front(); q.pop();
if(cur.y == N-1 && cur.x == N-1) {
answer = min(answer, cur.cost);
}
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int ny = cur.y + dy[i];
int nx = cur.x + dx[i];
if(ny <0 || nx < 0 || ny >= N || nx >= N || board[ny][nx] == 1)
continue;
int ncost = 0;
if(cur.dir != i) {
ncost = cur.cost + 600;
}
else {
ncost = cur.cost + 100;
}
if(MAP[i][ny][nx] >= ncost) {
POS next;
next.y = ny; next.x = nx; next.dir = i; next.cost = ncost;
q.push(next);
MAP[i][ny][nx] = ncost;
}
}
}
return answer;
}'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [2019 카카오 개발자 겨울 인턴십] 튜플 (0) | 2022.04.17 |
|---|---|
| [프로그래머스] 베스트 앨범 (c++) (0) | 2022.04.16 |
| [2021 카카오 채용형 인턴십] 표 편집 (lv 3) (0) | 2022.04.07 |
| [2021 카카오 채용연계형 인턴십] 거리두기 확인하기 (lv2) (0) | 2022.04.05 |
| [2022 Kakao blind recruitment] k진수에서 소수개수 구하기 (0) | 2022.03.30 |
Comments




