슈뢰딩거의 고등어
21609 상어중학교 본문
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/21609
21609번: 상어 중학교
상어 중학교의 코딩 동아리에서 게임을 만들었다. 이 게임은 크기가 N×N인 격자에서 진행되고, 초기에 격자의 모든 칸에는 블록이 하나씩 들어있고, 블록은 검은색 블록, 무지개 블록, 일반 블록
www.acmicpc.net
골드2
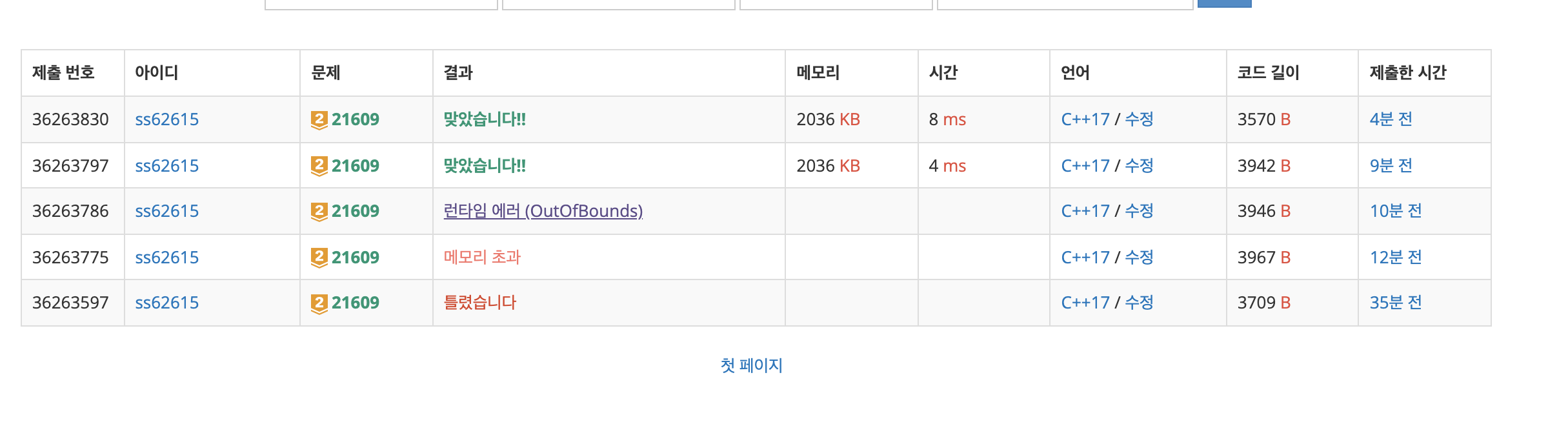
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct BLOCK_GROUP {
int m;
int y, x; // start pos
vector <pair <int, int>> v; // we can get size from here
int blank_cnt;
int block_cnt;
};
vector <BLOCK_GROUP> block_groups;
const int dy[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
const int dx[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int n, m, answer;
int arr[21][21];
int visit[21][21];
int max_block_size = 0;
vector <pair<int, int>> v;
// 기존 블록은 0 idx
bool compare (pair<int, int> a, pair <int, int> b) {
if(a.first == b.first)
return a.second < b.second;
return a.first < b.first;
}
bool compare_block_group(BLOCK_GROUP a, BLOCK_GROUP b) {
if (a.block_cnt == b.block_cnt) {
if(a.blank_cnt == b.blank_cnt) {
if(a.y == b.y)
return a.x > b.x;
else
return a.y > b.y;
}
else
return a.blank_cnt > b.blank_cnt;
}
return a.v.size() > b.v.size();
}
// get all block groups
void BFS(int y, int x) {
int value = arr[y][x];
int blank_cnt = 0;
int blocks = 1;
BLOCK_GROUP block_group;
block_group.y = y;
block_group.x= x;
block_group.m = value;
queue <pair<int, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(y, x));
visit[y][x] = true;
while(!q.empty()) {
int cy = q.front().first;
int cx = q.front().second;
q.pop();
// insert into block_group
block_group.v.push_back(make_pair(cy, cx));
if(arr[cy][cx] == 0)
blank_cnt++;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int ny = cy + dy[i];
int nx = cx + dx[i];
if(ny < 0 || ny >=n || nx < 0 || nx >= n)
continue;
if(visit[ny][nx] == false && (arr[ny][nx] == 0 || arr[ny][nx] == value)) {
q.push(make_pair(ny, nx));
visit[ny][nx] = true;
blocks++;
}
}
}
block_group.blank_cnt = blank_cnt;
block_group.block_cnt = blocks;
if(blocks >= 2)
block_groups.push_back(block_group);
}
void reset_rainbow_visit() {
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
if(arr[i][j] == 0)
visit[i][j] = false;
}
void gravity() {
// gravity
for(int x=0; x<n; x++) {
for(int y=n-2; y>=0; y--) {
// -1, -2 는 이동을 안해도 댐
if(arr[y][x] < 0)
continue;
int move = 0; // 바로 밑칸이랑 비교 움직일수 있다고 가정
// end || not -
while(true) {
move++;
if(arr[y+move][x] != -2 || y+move == n) {
move--;
break;
}
}
// 이동
arr[y+move][x] = arr[y][x];
if(move != 0)
arr[y][x] = -2;
}
}
}
void turn() {
// turn, copy
int tmp_arr[n][n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
tmp_arr[i][j] = arr[i][j];
memset(arr, -2, sizeof(arr));
for(int x=n-1,i=0; x>=0; x--, i++) {
for(int j=0, y=0; y<n; y++, j++) {
arr[i][j] = tmp_arr[y][x];
}
}
}
void solve() {
// 초기화
memset(visit, false, sizeof(visit));
block_groups.clear();
// get all block groups
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
if(arr[i][j] > 0 && visit[i][j] == false) {
BFS(i, j);
// 0 block visit 풀어주기
reset_rainbow_visit();
}
if(block_groups.size() == 0)
return;
sort(block_groups.begin(), block_groups.end(), compare_block_group);
int point = 0;
for(int i=0; i<block_groups[0].block_cnt; i++) {
int y = block_groups[0].v[i].first;
int x = block_groups[0].v[i].second;
arr[y][x] = -2; // empty
}
point = block_groups[0].block_cnt;
answer += (point*point);
gravity();
turn();
gravity();
solve();
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i][j]);
solve();
printf("%d\n", answer);
return 0;
}틀렸던 이유
1. visit 를 rainbow 블록은 매번 초기화를 해주어야함
왜? rainbow 블록은 중첩되어 탐색이 가능해야하기때문!!
2. 메모리 초과 : 크기가 2 미만인 블록은 저장할 필요가 없음
중력작용
void gravity() {
// gravity
for(int x=0; x<n; x++) {
for(int y=n-2; y>=0; y--) {
// -1, -2 는 이동을 안해도 댐
if(arr[y][x] < 0)
continue;
int move = 0; // 바로 밑칸이랑 비교 움직일수 있다고 가정
// end || not -
while(true) {
move++;
if(arr[y+move][x] != -2 || y+move == n) {
move--;
break;
}
}
// 이동
arr[y+move][x] = arr[y][x];
if(move != 0)
arr[y][x] = -2;
}
}
}90도 반시계 방향 회전
void turn() {
// turn, copy
int tmp_arr[n][n];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++)
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
tmp_arr[i][j] = arr[i][j];
memset(arr, -2, sizeof(arr));
for(int x=n-1,i=0; x>=0; x--, i++) {
for(int j=0, y=0; y<n; y++, j++) {
arr[i][j] = tmp_arr[y][x];
}
}
}'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 14499 주사위굴리기 (0) | 2021.12.19 |
|---|---|
| 13460 구슬탈출2 (0) | 2021.12.19 |
| 21608 상어초등학교 (0) | 2021.12.11 |
| 14888 연산자 끼워넣기 ( DFS : 중복순열 || next_permutation) (0) | 2021.12.10 |
| 17143 낚시왕 (0) | 2021.12.09 |
Comments

