| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
- 코테
- c++
- DFS
- 세브란스
- 부주상골수술후기
- dp
- SQLD
- 독일어
- 코딩테스트
- 부주상골증후군
- BFS
- 독학
- 롯데정보통신
- 구현
- SWIFT
- sql
- 카카오코테
- 백준
- 부주상골수술
- 카카오인턴십
- 카카오인턴
- 프로그래머스
- 스택
- ChatGPT
- IOS
- 부주상골
- 리눅스
- istringstream
- 분할정복
- 독일어독학
- Today
- Total
슈뢰딩거의 고등어
[백준] 17837 새로운 게임2 본문
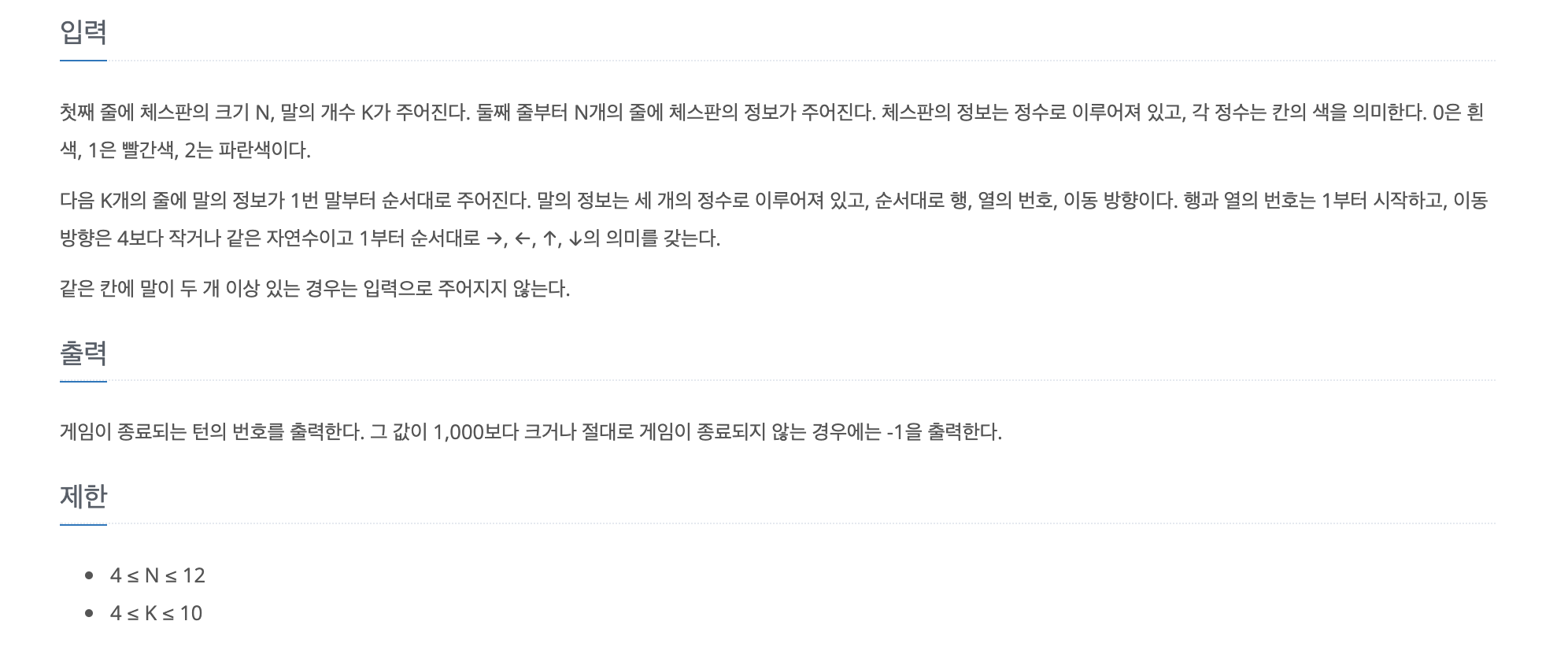
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/17837
17837번: 새로운 게임 2
재현이는 주변을 살펴보던 중 체스판과 말을 이용해서 새로운 게임을 만들기로 했다. 새로운 게임은 크기가 N×N인 체스판에서 진행되고, 사용하는 말의 개수는 K개이다. 말은 원판모양이고, 하
www.acmicpc.net

[풀이]
각 맵에 말들의 인덱스를 vector 해서 담을 수 있도록 한다.
각 말이 가지고 있어야 하는 정보는 위치(y, x), 방향(dir), 몇층(floor)이다.
struct MAL {
int y, x, floor, dir;
};
vector <MAL> mal; // 말들의 정보를 저장하는 vector
int map[13][13]; // 맵의 rbw 정보를 저장하는 맵
vector <int> ele[13][13]; // 맵에 존재하는 말들의 인덱스를 저장할 맵말을 하나하나 이동시킨다.
1. 말의 방향으로 새로 이동할 위치 ny, nx 를 구하고 이동하려는 위치의 (ny, nx) 가 파란색인지 맵의 안에 존재하는지 판단한다.
a) 파란색 or 맵의 안에 존재하지 않을 경우, 이동방향을 반대로 바꿔서 새로 ny, nx 를 갱신한다.
a-1) 새로운 ny, nx 도 파란색이거나 맵의 바깥에 있다면 이동시키지 않고 다음 말 순서로 넘어간다.
for(int i=0; i<k; i++) {
int y = mal[i].y;
int x = mal[i].x;
int dir = mal[i].dir;
int floor = mal[i].floor;
int ny = y + dy[dir];
int nx = x + dx[dir];
//blue
if(ny < 1 || ny > n || nx < 1 || nx > n || map[ny][nx] == 2) {
if(dir == 0 || dir == 2)
dir++;
else
dir--;
mal[i].dir = dir;
ny = y + dy[dir];
nx = x + dx[dir];
if(ny < 1 || ny > n || nx < 1 || nx > n || map[ny][nx] == 2) {// do not move
continue;
}
}
2. 현재위치(y, x)에 자신을 포함하여 자신 위에 놓인 말들을 target 벡터에 넣는다.
vector <int> target;
target.clear();
for(int i=ele[y][x].size()-1; i>=floor; i--) {
int mal_idx = ele[y][x][i];
target.push_back(mal_idx);
ele[y][x].pop_back();
}
3. 이동하려는 위치가 빨간색인지 하얀색인지 판단한다.
a) 빨간색일 경우 target 의 순서를 뒤집어서 ele[ny][nx]에 push_back 해준다.
// red
if(map[ny][nx] == 1) {
int height = ele[ny][nx].size()-1;
for(auto t: target) {
ele[ny][nx].push_back(t);
mal[t].y = ny;
mal[t].x = nx;
mal[t].floor = ++height;
}
}b) 하얀색일 경우 target 의 순서를 유지하여 ele[ny][nx]에 push_back 해준다.
// white
else if(map[ny][nx] == 0) {
int height = ele[ny][nx].size()-1;
for(int j=target.size()-1; j>=0; j--) {
ele[ny][nx].push_back(target[j]);
mal[target[j]].y = ny;
mal[target[j]].x = nx;
mal[target[j]].floor = ++height;
}
}c). 위에서 push_back 을 해주면서 옮기는 말들의 정보도 새로운 위치로 업데이트 해준다.
4. 말을 옮긴 ny, nx 의 위치에 존재하는 말들이 4개 이상일 경우 종료한다. 아닐 경우 다시 반복한다.
if (ele[ny][nx].size() >= 4) {
return;
}
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
const int dx[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
struct MAL {
int y, x, floor, dir;
};
vector <MAL> mal;
int n,k, answer;
int map[13][13];
vector <int> ele[13][13];
void solve() {
while(answer < 1000) {
answer++;
for(int i=0; i<k; i++) {
int y = mal[i].y;
int x = mal[i].x;
int dir = mal[i].dir;
int floor = mal[i].floor;
int ny = y + dy[dir];
int nx = x + dx[dir];
//blue
if(ny < 1 || ny > n || nx < 1 || nx > n || map[ny][nx] == 2) {
if(dir == 0 || dir == 2)
dir++;
else
dir--;
mal[i].dir = dir;
ny = y + dy[dir];
nx = x + dx[dir];
if(ny < 1 || ny > n || nx < 1 || nx > n || map[ny][nx] == 2) {// do not move
continue;
}
}
vector <int> target;
target.clear();
for(int i=ele[y][x].size()-1; i>=floor; i--) {
int mal_idx = ele[y][x][i];
target.push_back(mal_idx);
ele[y][x].pop_back();
}
// red
if(map[ny][nx] == 1) {
int height = ele[ny][nx].size()-1;
for(auto t: target) {
ele[ny][nx].push_back(t);
mal[t].y = ny;
mal[t].x = nx;
mal[t].floor = ++height;
}
}
// white
else if(map[ny][nx] == 0) {
int height = ele[ny][nx].size()-1;
for(int j=target.size()-1; j>=0; j--) {
ele[ny][nx].push_back(target[j]);
mal[target[j]].y = ny;
mal[target[j]].x = nx;
mal[target[j]].floor = ++height;
}
}
if (ele[ny][nx].size() >= 4) {
return;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &k);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(int j=1; j<=n; j++) {
scanf("%d", &map[i][j]);
}
for(int i=0; i<k; i++) {
MAL tmp;
scanf("%d %d %d", &tmp.y, &tmp.x, &tmp.dir);
tmp.dir--; tmp.floor = 0;
mal.push_back(tmp);
ele[tmp.y][tmp.x].push_back(i); // 말의 번호를 push_back
}
solve();
if(answer >= 1000)
printf("-1\n");
else
printf("%d\n", answer);
}'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 정렬 (vector, sort) (0) | 2022.02.08 |
|---|---|
| DFS (순열, 조합) (0) | 2022.02.08 |
| [프로그래머스] SQL 고득점 키트 (0) | 2022.02.04 |
| [백준] 14916 거스름돈 (DP) (0) | 2022.02.04 |
| [백준] 1010 다리놓기 (조합의 수) n개에서 m개 뽑기 (0) | 2022.02.03 |

